How To Open A Foreign Bank Account? This seemingly straightforward question opens a door to a world of international finance, brimming with opportunities and complexities. From understanding the diverse documentation requirements across countries to navigating the nuances of different account types and banking systems, the journey to securing a foreign bank account requires careful planning and execution. This guide provides a comprehensive roadmap, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate this process and unlock the benefits of international banking.
We’ll explore the essential steps, from selecting the right bank and account type to managing your account effectively and understanding the crucial tax and legal implications. We’ll also delve into practical examples and address common challenges, providing clear, actionable advice to help you achieve your international banking goals. Whether you’re a seasoned global traveler or just starting to explore international financial options, this guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge you need.
Understanding Requirements for Opening a Foreign Bank Account
Opening a foreign bank account can offer numerous benefits, from diversifying assets to accessing international markets. However, the process varies significantly depending on your nationality, the country where you’re opening the account, and the type of account you need. Understanding the specific requirements is crucial for a smooth and successful application.
Documentation Needed to Open a Foreign Bank Account
Typically, you’ll need a comprehensive set of documents to verify your identity and financial standing. This usually includes a valid passport or national ID card, proof of address (recent utility bill or bank statement), and evidence of your source of funds (tax returns, employment contracts, or investment statements). Some banks may also request additional documentation, such as a letter of reference from your current bank or a completed application form specific to their institution.
The exact requirements can vary considerably, and it’s always best to check directly with the bank you intend to use.
Variations in Required Documentation Across Countries
The specific documentation needed can differ substantially based on the country’s regulations and the bank’s internal policies. For instance, in some countries within the European Union, a standardized KYC (Know Your Customer) process is followed, requiring similar documentation across different banks. However, in other jurisdictions, the requirements may be more stringent or involve additional paperwork. Countries with stricter anti-money laundering (AML) regulations often require more extensive due diligence, including detailed information about the purpose of the account and the source of funds.
For example, opening an account in the United States might require a US tax identification number (TIN) or Social Security Number (SSN), whereas in Switzerland, specific documentation relating to tax residency might be necessary.
Account Opening Processes for Different Account Types
The process for opening a personal account differs from that of a business account. Personal accounts typically require documentation proving your identity and address, along with information about your employment and income. Business accounts, on the other hand, demand significantly more documentation. This usually includes articles of incorporation, business registration certificates, details of the company’s directors and shareholders, and financial statements demonstrating the business’s financial health and stability.
Furthermore, the level of scrutiny applied during the due diligence process is often greater for business accounts due to increased AML/CFT (Combating the Financing of Terrorism) concerns.
Minimum Deposit Requirements for Several Major International Banks
The minimum deposit required to open an account varies greatly between banks and account types. Some banks may not have a minimum deposit requirement, while others may require substantial sums, especially for premium accounts. The following table provides a comparison, but it’s crucial to verify the current requirements directly with each bank as these amounts can change.
| Bank | Country | Personal Account Minimum Deposit (USD) | Business Account Minimum Deposit (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSBC | Various | 0 | Varies by location and account type |
| Citibank | Various | Varies by location | Varies by location and account type |
| Standard Chartered | Various | Varies by location | Varies by location and account type |
| DBS Bank | Singapore | Varies by account type | Varies by account type |
Managing Your Foreign Bank Account

Successfully opening a foreign bank account is only the first step. Effective management is crucial to ensure your funds are secure and accessible. This section details the key aspects of managing your international finances, from transferring money to mitigating risks and understanding associated fees.
Money Transfers to and From Your Foreign Account
Several methods exist for transferring funds to and from your foreign bank account. Wire transfers are a common option, offering speed and security but often incurring higher fees. Online banking platforms increasingly provide international transfer capabilities, often at lower costs. Consider using a dedicated international money transfer service, which may offer competitive exchange rates and transparent fees.
The choice of method depends on factors like the transfer amount, urgency, and cost considerations. For example, a large sum transferred urgently might justify the higher cost of a wire transfer, while smaller, less time-sensitive transfers might benefit from the lower cost of an online service.
Securing Your Foreign Bank Account and Protecting Your Funds
Protecting your foreign bank account requires a multi-layered approach. Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are essential to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly monitor your account statements for any suspicious activity, and report any discrepancies immediately to your bank. Consider utilizing fraud alerts and transaction monitoring tools offered by your bank. Furthermore, understanding the bank’s security protocols and adhering to them is vital.
For instance, be wary of phishing scams that attempt to obtain your login credentials.
Common Fees Associated with Maintaining a Foreign Bank Account
Maintaining a foreign bank account often involves various fees. These can include monthly maintenance fees, account opening fees, international transfer fees, and foreign transaction fees. Exchange rate markups can also significantly impact the cost of transfers. It’s crucial to carefully review the bank’s fee schedule before opening an account to understand the total cost of ownership. Banks may also charge fees for inactivity if the account remains dormant for an extended period.
Comparing fee structures across different banks is advisable to find the most cost-effective option.
Tips for Managing International Transactions Effectively
Effective management of international transactions requires careful planning and attention to detail.
- Understand exchange rates: Fluctuations in exchange rates can significantly impact the value of your transfers. Monitor exchange rates and consider transferring funds when rates are favorable.
- Choose the right transfer method: Select the transfer method that best suits your needs in terms of speed, cost, and security.
- Keep accurate records: Maintain detailed records of all transactions, including dates, amounts, and fees.
- Be aware of potential fees: Familiarize yourself with all associated fees before initiating a transaction.
- Utilize secure payment methods: Opt for secure payment methods like wire transfers or reputable online platforms to minimize the risk of fraud.
- Regularly review your account statements: Promptly identify and address any discrepancies or unauthorized transactions.
Tax Implications and Legal Considerations: How To Open A Foreign Bank Account
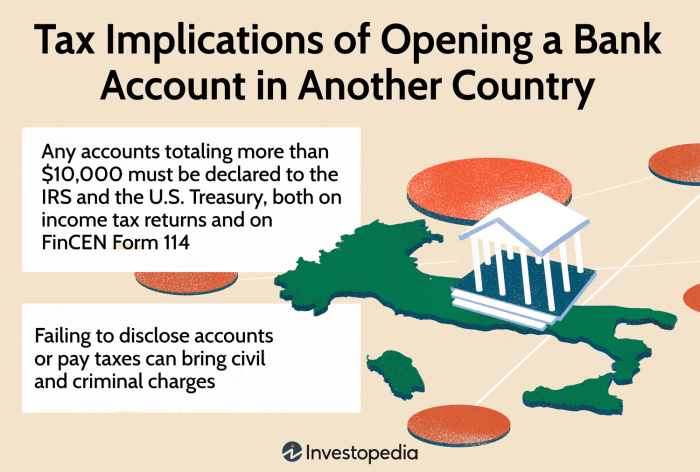
Opening a foreign bank account introduces complexities beyond managing your finances. Understanding the tax implications and legal ramifications is crucial to avoid potential penalties and maintain compliance with international regulations. Failure to do so can result in significant financial and legal repercussions.
Tax Implications of Holding a Foreign Bank Account
The tax implications of holding a foreign bank account vary significantly depending on your country of residence and the specific account type. Many countries require the reporting of foreign accounts, even if no income is generated directly from the account itself. This reporting often involves disclosing the account’s existence, balance, and any transactions exceeding a certain threshold. Furthermore, any interest earned, dividends received, or capital gains generated from assets held within the foreign account are typically subject to taxation in your home country, even if already taxed in the foreign jurisdiction.
Double taxation treaties between countries often mitigate this, but careful planning is essential. Failure to report foreign accounts accurately and timely can lead to substantial penalties and legal action.
Compliance with Relevant Regulations and Laws
Complying with relevant regulations and laws related to foreign bank accounts is paramount. This involves understanding the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) in the US, the Common Reporting Standard (CRS) adopted by many OECD countries, and any specific regulations within your country of residence and the country where the bank is located. These regulations often mandate the reporting of foreign financial assets to tax authorities.
Understanding and adhering to these regulations is vital to avoid severe penalties. Seek professional advice from a tax advisor or financial professional specializing in international taxation to ensure full compliance.
Potential Legal Issues and Avoidance Strategies
Potential legal issues arising from foreign bank accounts can range from tax evasion charges to money laundering accusations. Maintaining accurate records of all transactions, ensuring compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, and seeking professional advice are crucial steps in mitigating risks. For example, failing to report foreign income or intentionally structuring transactions to avoid tax reporting requirements could lead to significant legal consequences.
Transparency and proper documentation are key to avoiding such issues. Similarly, using a foreign bank account for illicit activities, such as money laundering or financing terrorism, carries severe legal ramifications, including hefty fines and imprisonment.
Tax Reporting Requirements in Different Countries, How To Open A Foreign Bank Account
The following table summarizes the tax reporting requirements for foreign bank accounts in three different countries. Note that these are simplified examples and specific requirements may vary depending on individual circumstances. Always consult with a tax professional for personalized guidance.
| Country | Reporting Threshold | Reporting Form | Penalty for Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Generally, accounts with a total aggregate value exceeding $10,000 at any point during the year | FinCEN Form 114 (FBAR) and relevant tax forms | Significant penalties, including civil penalties and potential criminal prosecution |
| United Kingdom | Accounts with a balance exceeding £50,000 at any point during the tax year | Self-Assessment tax return | Penalties can include surcharges, interest charges, and potential prosecution |
| Canada | Accounts with a balance exceeding CAD100,000 at any point during the tax year | T1135, Report of Foreign Income and Property | Penalties vary, but can include interest charges and potential prosecution |
Opening a foreign bank account successfully hinges on meticulous preparation and a thorough understanding of the process. By carefully considering your needs, researching different banks and account types, and meticulously completing the application, you can unlock access to a wider range of financial services and opportunities. Remember, understanding the tax and legal implications is paramount, ensuring compliance and avoiding potential pitfalls.
With careful planning and the information provided in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the intricacies of international banking and confidently manage your global finances.

