How To Set Up An Offshore Account: Navigating the world of offshore banking can seem daunting, but understanding the process, benefits, and risks is key to making informed decisions. This comprehensive guide unravels the complexities, providing a clear path to establishing and managing your offshore account effectively and legally. We’ll explore various account types, optimal jurisdictions, the application process, and crucial security measures, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently navigate this specialized financial landscape.
From selecting the right jurisdiction based on your financial goals and risk tolerance to understanding the legal and tax implications, we’ll cover every step. We’ll delve into the intricacies of transferring funds, maintaining account security, and complying with international regulations. Real-world examples and case studies will illuminate the practical applications of offshore accounts, helping you understand how they can be utilized for legitimate purposes, such as international business, asset protection, and investment diversification.
Choosing a Jurisdiction: How To Set Up An Offshore Account

Selecting the right offshore banking jurisdiction is crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with holding assets outside your home country. The ideal location depends heavily on individual circumstances, including financial goals, risk tolerance, and the nature of the assets being held. Careful consideration of various factors is essential to ensure a secure and compliant setup.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Offshore Banking Location
Several key factors influence the choice of an offshore banking jurisdiction. These include the jurisdiction’s regulatory framework, its political and economic stability, its tax laws, the availability of banking services, and the level of confidentiality offered. A thorough assessment of these elements is necessary to determine the best fit for individual needs. For instance, a jurisdiction with stringent anti-money laundering (AML) regulations might be preferred by those seeking a high level of security, while a jurisdiction with more lenient tax laws might be attractive to those seeking tax optimization strategies.
The availability of specific banking services, such as private wealth management or trust services, is also a crucial consideration.
Regulatory Environment of Popular Offshore Jurisdictions
Popular offshore jurisdictions each have their unique regulatory environments. The Cayman Islands, for example, are known for their robust regulatory framework and commitment to international standards on AML and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT). They boast a sophisticated financial infrastructure and a strong reputation for stability. Conversely, jurisdictions like the British Virgin Islands (BVI) might offer a more flexible regulatory approach, but this might come with a slightly higher risk profile.
Understanding the nuances of each jurisdiction’s regulations is crucial for compliance and avoiding potential legal issues. This includes understanding the specific requirements for reporting transactions, maintaining accurate records, and adhering to Know Your Customer (KYC) guidelines.
Key Criteria for Evaluating the Stability and Security of a Jurisdiction
The stability and security of a chosen jurisdiction are paramount. Key criteria for evaluation include the jurisdiction’s political stability, its economic strength, the strength of its legal system, and the independence of its judiciary. A politically stable jurisdiction with a strong economy and a well-established legal system offers greater security for assets. The independence of the judiciary ensures that legal disputes are resolved fairly and impartially, protecting the interests of account holders.
Factors such as the country’s credit rating, its level of corruption, and the presence of any significant geopolitical risks should also be considered. For example, a jurisdiction with a high credit rating and a low level of corruption is generally considered more stable and secure.
Pros and Cons of Top Offshore Banking Locations, How To Set Up An Offshore Account
The decision of where to establish an offshore account requires weighing the advantages and disadvantages of various locations.
It is important to note that this is not an exhaustive list and the suitability of a particular jurisdiction will depend on individual circumstances. Always consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any decisions.
- Cayman Islands:
- Pros: Strong regulatory framework, political stability, sophisticated financial infrastructure, well-established legal system.
- Cons: Higher costs compared to some other jurisdictions, stricter regulatory compliance requirements.
- British Virgin Islands (BVI):
- Pros: Relatively low costs, flexible regulatory environment, popular for asset protection structures.
- Cons: Potentially higher risk profile due to less stringent regulations compared to some other jurisdictions.
- Switzerland:
- Pros: Strong banking secrecy laws (though increasingly regulated), political stability, well-developed financial sector.
- Cons: High costs, stringent Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
The Account Opening Process
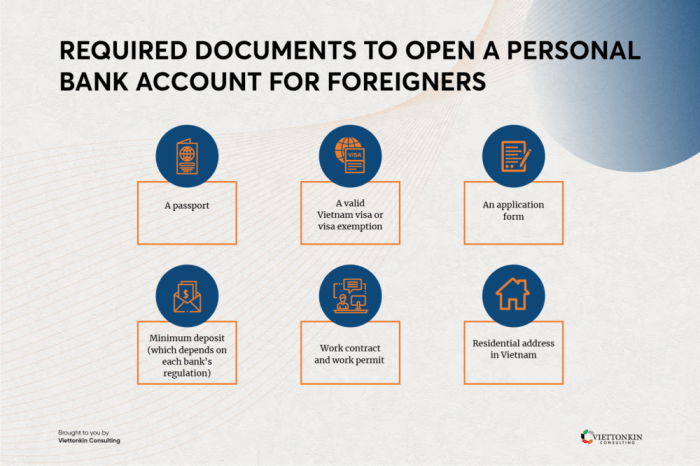
Opening an offshore bank account involves a multi-step process that requires careful preparation and adherence to strict regulatory guidelines. The specific requirements vary depending on the chosen jurisdiction and the bank itself, but several common steps and documentation requirements generally apply. Understanding these steps beforehand is crucial for a smooth and efficient account opening experience.
The process typically begins with preliminary inquiries and progresses through application submission, due diligence checks, and finally, account activation. Each stage requires precise documentation and a clear understanding of the bank’s procedures. Failure to provide complete and accurate information can lead to delays or rejection of the application.
Required Documentation
Offshore banks employ rigorous due diligence procedures to comply with international anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. Consequently, the application process demands comprehensive documentation to verify the applicant’s identity, source of funds, and intended use of the account.
The specific documents required can vary, but typically include:
- A valid, government-issued passport or national identity card.
- Proof of address, such as a recent utility bill or bank statement.
- Completed account application form, including details about the purpose of the account.
- Proof of funds demonstrating the source and legitimacy of the funds to be deposited.
- Reference letters from previous banks or financial institutions.
- Depending on the jurisdiction and the amount involved, additional documentation might be requested, such as business registration documents for corporate accounts.
Due Diligence Procedures
Offshore banks undertake extensive due diligence to mitigate risks associated with money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes. This process involves verifying the applicant’s identity, assessing the risk profile of the account, and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity.
These procedures often include:
- Identity verification: Banks cross-reference provided identification documents with official databases to confirm authenticity and prevent identity theft.
- Source of funds verification: Banks scrutinize documentation to ensure that the funds being deposited originate from legitimate sources and are not derived from illegal activities.
- Background checks: In certain cases, banks may conduct background checks on the applicant to assess their financial history and reputation.
- Ongoing monitoring: Once the account is opened, banks continue to monitor transactions for any suspicious activity that might indicate illegal financial activity.
Account Opening Process Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates a typical offshore bank account opening process. Note that this is a generalized representation, and the specific steps and timelines may vary depending on the bank and jurisdiction.
Imagine a flowchart with the following boxes and arrows:
- Start -> Arrow to box 2
- Initial Inquiry & Consultation -> Arrow to box 3
- Application Submission (with required documents) -> Arrow to box 4
- Bank’s Due Diligence & Verification -> Arrow to box 5
- Account Approval/Rejection -> Arrow to box 6 (Approval goes to box 7, Rejection goes to box 8)
- Account Activation & Funding -> Arrow to box 9
- Account Opened -> Arrow to box 10
- Application Rejected (Reasons provided) -> Arrow to box 10
- End
Illustrative Examples of Offshore Account Use Cases
Offshore accounts, when used correctly, offer various legitimate benefits for individuals and businesses. Understanding these legitimate uses is crucial to dispel misconceptions and highlight the responsible application of offshore financial structures. The following examples illustrate how offshore accounts can be utilized for diverse purposes, always within the framework of legal and ethical compliance.
Legitimate Business Use of Offshore Accounts
A multinational corporation, “GlobalTech Solutions,” operates in several countries. To streamline international transactions and manage its global finances efficiently, GlobalTech establishes an offshore account in a jurisdiction with favorable tax treaties and robust banking regulations. This account facilitates seamless cross-border payments to suppliers, employees, and investors, minimizing transaction fees and simplifying complex financial reporting across multiple jurisdictions. The account’s transparency and adherence to international financial reporting standards ensure complete compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Offshore Accounts for Asset Protection
Imagine a successful entrepreneur, Ms. Anya Petrova, who owns a thriving technology startup. To protect her personal assets from potential lawsuits related to her business, she establishes an offshore trust in a jurisdiction known for strong asset protection laws. This trust holds a significant portion of her wealth, shielding it from creditors in the event of unforeseen legal challenges.
The trust is managed by independent trustees, ensuring the assets remain protected while adhering to all legal and ethical guidelines. This strategy, while proactive, prioritizes the long-term security of her assets.
Case Study: Offshore Banking Benefits for a Freelancer
Mr. David Chen, a freelance software developer based in the United States, earns a significant portion of his income from international clients. He establishes an offshore account in a jurisdiction with a favorable tax regime for freelancers. This account allows him to efficiently manage his international payments, reducing tax burdens and simplifying his financial reporting. By meticulously tracking his income and expenses and ensuring compliance with US tax laws, Mr.
Chen leverages the offshore account to optimize his financial situation without engaging in any illicit activities. His strategy is a testament to how proper planning and adherence to regulations can enhance financial well-being.
International Investment Strategies with Offshore Accounts
An investment firm, “Vanguard Global Investments,” uses offshore accounts to facilitate investments in diverse international markets. This allows them to diversify their portfolio, minimizing risk and maximizing returns. The offshore accounts provide efficient access to various investment vehicles, including international stocks, bonds, and real estate. The firm adheres to strict regulatory compliance in all jurisdictions where it operates, ensuring transparency and accountability in its investment strategies.
This exemplifies how offshore accounts can be a powerful tool for sophisticated international investment management.
Setting up an offshore account requires careful planning and a thorough understanding of the legal and financial landscape. This guide has provided a framework for navigating this complex process, from choosing the appropriate jurisdiction and completing the application to managing your account securely and complying with relevant regulations. Remember, seeking professional advice from financial and legal experts is crucial before embarking on this journey.
By understanding the intricacies involved and taking the necessary precautions, you can leverage the potential benefits of offshore banking while mitigating associated risks.

