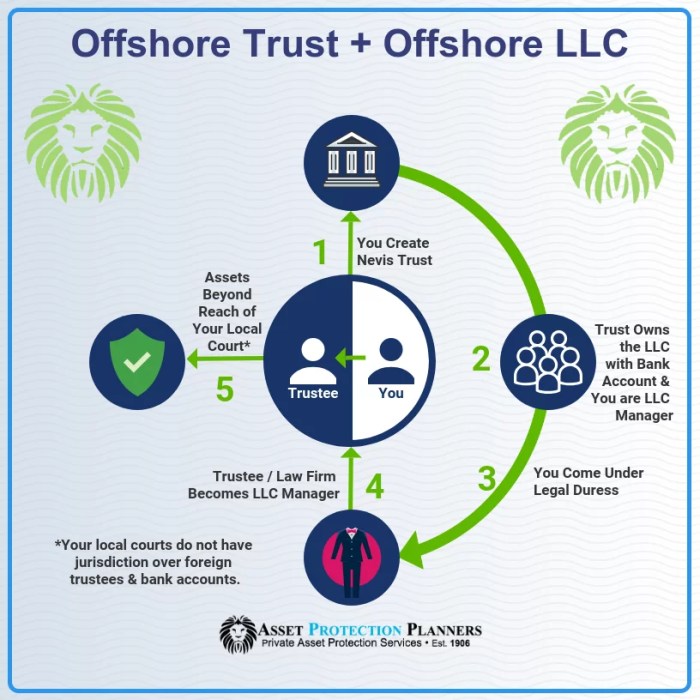
Offshore Trust Companies offer a compelling solution for individuals and businesses seeking sophisticated asset protection and wealth management strategies. These entities, operating outside the jurisdiction of the trust’s creators, provide a layer of legal and financial privacy often unavailable through domestic structures. This guide delves into the intricacies of offshore trust companies, exploring their functionalities, jurisdictional variations, associated risks, and the due diligence required for selection.
Understanding the nuances of offshore trust companies requires navigating complex legal and financial landscapes. From establishing the trust itself to selecting the appropriate jurisdiction and managing the associated tax implications, the process demands careful consideration. This exploration aims to illuminate the key aspects, providing readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions.
Jurisdictional Considerations
Choosing the right jurisdiction for establishing an offshore trust is crucial, impacting tax liabilities, regulatory compliance, and overall asset protection. Several factors must be considered, including the legal framework governing trusts, the tax regime applicable to trust assets and distributions, and the level of regulatory oversight. The selection process should be guided by a thorough understanding of these jurisdictional nuances and a careful assessment of individual circumstances.
Key Jurisdictions for Offshore Trusts
Several jurisdictions have established themselves as popular choices for establishing offshore trusts. These jurisdictions typically offer attractive legal frameworks, favorable tax environments, and robust regulatory systems. The specific advantages of each jurisdiction vary, and the optimal choice depends on the individual needs and objectives of the trust settlor. Popular jurisdictions include the British Virgin Islands (BVI), the Cayman Islands, Bermuda, and Jersey.
These jurisdictions offer a combination of established legal precedents, political stability, and confidentiality provisions that make them attractive to high-net-worth individuals and businesses.
Tax Implications of Offshore Trust Companies
The tax implications of using offshore trust companies vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction of incorporation and the residency status of the settlor, beneficiaries, and the trust itself. Some jurisdictions offer tax neutrality, meaning that the trust itself is not subject to direct taxation on its income or capital gains. However, the beneficiaries may be liable for tax on distributions received, depending on their tax residency.
Other jurisdictions may impose specific taxes on trusts, such as stamp duty or annual fees. It is crucial to seek professional tax advice to understand the potential tax consequences in the chosen jurisdiction and to ensure compliance with all relevant tax laws. For instance, a trust established in the BVI might not be directly taxed on its income, but the beneficiaries residing in the US might still be subject to US taxation on distributions received.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory environment for offshore trust companies varies across jurisdictions. Some jurisdictions have stringent regulatory frameworks with robust oversight from financial regulators, while others have less stringent rules. Compliance requirements often include maintaining detailed records, conducting regular audits, and adhering to anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines and even criminal charges.
Jurisdictions like Jersey and Guernsey, known for their robust regulatory frameworks, attract clients who value transparency and strong regulatory oversight. These jurisdictions often have stricter requirements regarding the identification of beneficiaries and the prevention of illicit activities.
Comparative Analysis of Jurisdictions
The following table compares four jurisdictions commonly used for establishing offshore trusts:
| Jurisdiction | Legal Framework | Tax Benefits | Regulatory Oversight |
|---|---|---|---|
| British Virgin Islands (BVI) | Well-established common law system, flexible trust legislation | Generally no direct taxation on trust income or capital gains | Financial Services Commission (FSC) regulates trust companies |
| Cayman Islands | Common law jurisdiction with modern trust legislation | No direct taxation on trust income or capital gains | Cayman Islands Monetary Authority (CIMA) regulates trust companies |
| Bermuda | Common law jurisdiction with specific trust legislation | No direct taxation on trust income or capital gains; however, specific taxes may apply to certain transactions. | Bermuda Monetary Authority (BMA) regulates trust companies |
| Jersey | Well-established common law system with robust trust legislation | No direct taxation on trust income or capital gains; however, specific taxes may apply to certain transactions. | Jersey Financial Services Commission (JFSC) regulates trust companies; known for its strong AML/KYC compliance standards. |
Services Offered by Offshore Trust Companies
Offshore trust companies provide a wide array of services designed to manage and protect assets for high-net-worth individuals and families. These services extend beyond simple asset holding, encompassing sophisticated financial planning and legal strategies aimed at minimizing tax liabilities, safeguarding assets from creditors, and ensuring efficient estate planning. The specific services offered can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the company itself, but there are common themes across the industry.Offshore trust companies assist clients with a variety of complex financial and legal matters.
Their expertise allows for the strategic management of assets across international borders, often offering solutions tailored to specific circumstances and goals. This involves understanding the nuances of different legal and tax systems, a crucial aspect of successful offshore trust management.
Asset Protection Services, Offshore Trust Companies
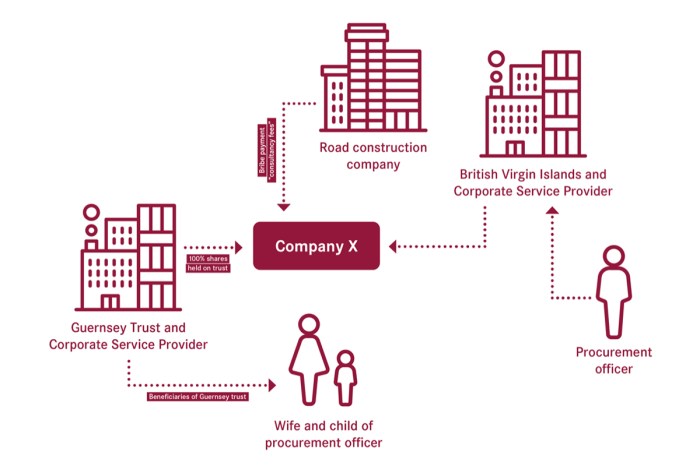
Offshore trust companies offer robust asset protection strategies. These strategies leverage the legal frameworks of different jurisdictions to shield assets from various threats, including creditors, lawsuits, and even political instability in the client’s home country. For example, a properly structured offshore trust in a jurisdiction with strong asset protection laws can prevent creditors from accessing assets held within the trust, even if the settlor (the person establishing the trust) faces financial difficulties.
This protection is often enhanced by the confidentiality provisions associated with certain offshore jurisdictions. Another example is the protection against potential expropriation of assets in politically unstable regions; holding assets within an offshore trust can mitigate this risk significantly.
Estate Planning Services
Offshore trust companies play a crucial role in international estate planning. They assist in creating and managing trusts that efficiently transfer wealth across generations while minimizing estate taxes and other inheritance-related costs. This often involves working with legal and tax professionals to ensure compliance with both the settlor’s home country laws and the laws of the jurisdiction where the trust is established.
Careful planning can minimize inheritance taxes, simplify the probate process, and ensure the smooth transfer of assets to beneficiaries according to the settlor’s wishes. For instance, a family with significant international holdings might use an offshore trust to manage assets in different countries, simplifying tax compliance and avoiding complex cross-border inheritance procedures.
Common Services Offered by Offshore Trust Companies
The following is a list of common services offered by offshore trust companies:
- Trust formation and administration
- Asset protection planning
- Estate and succession planning
- Tax optimization strategies (within legal and ethical parameters)
- Wealth management and investment services
- Fiduciary services (acting as trustee or protector)
- Company formation and administration
- International tax compliance
- Dispute resolution and litigation support
- Family office services
Due Diligence and Selection of an Offshore Trust Company: Offshore Trust Companies
Selecting an offshore trust company requires meticulous due diligence. The ramifications of choosing an unsuitable provider can be significant, impacting the security of your assets, the efficacy of your trust structure, and your overall financial well-being. A thorough vetting process is crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure the long-term success of your trust arrangements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Offshore Trust Company
The selection of an offshore trust company should be based on a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors. Ignoring any of these could lead to unforeseen complications and potentially jeopardize your trust’s objectives. A balanced approach, considering both qualitative and quantitative aspects, is essential.
- Jurisdictional Reputation and Regulatory Framework: The jurisdiction’s legal and regulatory environment significantly impacts the trust’s stability and protection. Consider jurisdictions known for robust regulatory oversight, strong asset protection laws, and a stable political climate. For example, jurisdictions like the Cayman Islands, British Virgin Islands, and Jersey are often preferred for their established trust structures and regulatory frameworks.
- Company Reputation and Track Record: Research the company’s history, focusing on its longevity, client testimonials, and any past regulatory actions or legal disputes. Look for a company with a proven track record of successful trust administration and a strong reputation within the industry.
- Financial Stability and Security: Assess the company’s financial health by examining its audited financial statements, credit rating, and insurance coverage. A financially stable company is less likely to experience operational disruptions that could affect your trust.
- Expertise and Specialization: Determine if the company possesses the specific expertise needed to manage your type of trust. Some companies specialize in particular areas, such as international trusts, family trusts, or charitable trusts.
- Fees and Charges: Obtain detailed information on all fees and charges associated with establishing and administering the trust. Compare fees across different providers to ensure you are receiving competitive pricing.
- Service Quality and Responsiveness: Evaluate the company’s communication style, responsiveness to inquiries, and overall client service quality. Regular communication and efficient service are crucial for effective trust management.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Inquire about the company’s technology infrastructure and its ability to provide secure online access to trust information and documentation. Modern technology is vital for efficient and transparent trust management.
Evaluating Reputation and Financial Stability
Thorough due diligence requires a multifaceted approach to assessing both reputation and financial stability. Independent verification of information is crucial to avoid relying solely on self-reported data.
- Independent Reviews and Ratings: Consult independent financial rating agencies and review websites specializing in offshore financial services. These resources provide objective assessments of companies’ financial health and reputation.
- Regulatory Compliance and Audits: Verify the company’s compliance with relevant regulations and the frequency of its financial audits. Regular audits by reputable accounting firms demonstrate a commitment to transparency and accountability.
- Client Testimonials and References: Seek out client testimonials and references to gauge the company’s reputation and service quality. Contacting previous clients directly can provide valuable insights into their experiences.
- Professional Affiliations and Accreditations: Look for professional affiliations and accreditations, which indicate a commitment to industry best practices and ethical conduct. Membership in reputable professional organizations can signal a higher level of trust and credibility.
Creating a Due Diligence Checklist
A structured checklist ensures a comprehensive and systematic approach to due diligence. This helps to avoid overlooking critical aspects and promotes a more efficient evaluation process. The checklist should be tailored to your specific needs and the complexity of your trust arrangements.
A sample checklist might include:
- Jurisdiction’s legal and regulatory framework review
- Company’s history, track record, and reputation research
- Financial statement analysis and credit rating check
- Assessment of company expertise and specialization
- Detailed review of fees and charges
- Evaluation of service quality and responsiveness
- Review of technology and infrastructure
- Verification of regulatory compliance and audits
- Collection and analysis of client testimonials and references
- Verification of professional affiliations and accreditations
Successfully navigating the world of offshore trust companies hinges on meticulous planning and a thorough understanding of the legal and financial intricacies involved. While the potential benefits—from enhanced asset protection to streamlined estate planning—are significant, the inherent risks necessitate careful due diligence and the selection of a reputable provider. This guide serves as a starting point for those seeking to leverage the power of offshore trusts, emphasizing the importance of professional advice throughout the process.
Remember, informed decisions are crucial for realizing the full potential of these sophisticated financial tools while mitigating potential pitfalls.