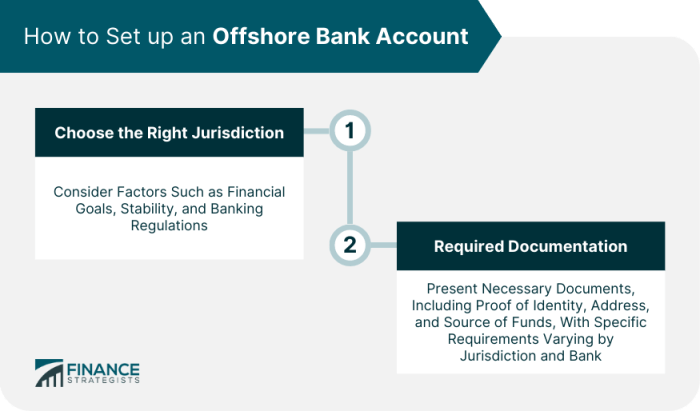
Setting Up An Offshore Bank Account opens doors to global finance, but navigating the complexities of international banking requires careful planning. This guide unravels the legal intricacies, explores optimal jurisdictions, and details the account opening process, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. We’ll delve into the benefits and risks, addressing common misconceptions and providing actionable strategies for managing your offshore account effectively and securely.
Understanding the regulatory landscape, choosing the right jurisdiction, and adhering to best practices are crucial for a successful and compliant offshore banking experience.
From understanding the legal frameworks and regulatory requirements in various jurisdictions to navigating the account opening process and managing your funds, this comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach. We’ll compare different offshore banking centers, analyze the implications of tax laws and banking secrecy, and highlight potential risks and considerations. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to establish and maintain an offshore bank account while mitigating potential challenges.
Legality and Regulations of Offshore Banking: Setting Up An Offshore Bank Account
Offshore banking, while often shrouded in mystery, operates within a complex web of international laws and regulations. Understanding these frameworks is crucial for anyone considering opening an offshore account, as non-compliance can lead to severe legal and financial repercussions. This section will clarify the legal landscape of offshore banking, highlighting key aspects of regulation and due diligence.
Legal Frameworks Governing Offshore Banking
Various jurisdictions boast robust legal frameworks governing offshore banking activities. These frameworks typically encompass anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations, tax information exchange agreements (TIEAs), and specific banking laws tailored to the offshore environment. The specific regulations vary widely depending on the jurisdiction, reflecting differences in economic priorities and risk tolerance. Some jurisdictions prioritize attracting foreign investment by offering relaxed regulations, while others maintain stricter controls to prevent illicit financial activities.
The level of transparency and regulatory oversight significantly influences a jurisdiction’s reputation and attractiveness to both legitimate and illegitimate businesses.
Regulatory Requirements Comparison: Three Offshore Banking Centers
A comparison of regulatory requirements across three prominent offshore banking centers – the Cayman Islands, Switzerland, and Singapore – illustrates the diversity of approaches. The Cayman Islands, known for its secrecy until recently, now adheres to international standards through various TIEAs and AML regulations, though certain aspects of its legal framework remain less transparent than others. Switzerland, while historically a haven for private banking, has significantly enhanced its regulatory framework in recent years, particularly concerning transparency and tax compliance.
Singapore, on the other hand, adopts a more proactive and stringent regulatory approach, maintaining high standards of AML compliance and financial transparency to safeguard its reputation as a leading international financial center. These differences underscore the importance of researching specific jurisdictional requirements before establishing an offshore account.
Due Diligence Processes in Offshore Bank Account Opening
Opening an offshore bank account involves rigorous due diligence procedures. Banks are legally obligated to verify the identity and source of funds of all account holders. This typically involves providing extensive documentation, including proof of identity, address, source of wealth, and purpose of the account. Banks may also conduct enhanced due diligence (EDD) for high-risk clients or transactions.
This may involve requesting additional documentation, conducting background checks, and monitoring account activity closely. The due diligence process aims to prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities, ensuring compliance with international regulations. Failure to meet these requirements can result in account rejection or even legal penalties.
Common Misconceptions Regarding Offshore Banking Legality, Setting Up An Offshore Bank Account
Several misconceptions surround the legality of offshore banking. One common misconception is that all offshore banking is inherently illegal. In reality, many individuals and businesses legitimately use offshore accounts for various purposes, such as asset protection, international trade, and tax optimization (within legal limits). Another misconception is that offshore accounts automatically shield assets from taxation. While some jurisdictions offer favorable tax environments, it is crucial to understand and comply with all relevant tax laws in one’s country of residence.
Failing to declare offshore income can lead to severe tax penalties and legal repercussions. Finally, the belief that offshore accounts provide complete anonymity is false; stricter regulations globally necessitate greater transparency in offshore banking.
Tax Implications of Offshore Accounts
| Country | Tax Residency Rules | Tax Reporting Requirements | Potential Tax Benefits/Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Citizens and Green Card holders are taxed on worldwide income. | Foreign bank account reporting (FBAR) and Form 8938 are required. | Limited tax benefits; significant penalties for non-compliance. |
| United Kingdom | Tax residency based on several factors, including time spent in the UK. | Offshore income must be declared. | Tax treaties may offer some relief, but generally, offshore income is taxable. |
| Cayman Islands | No direct taxation on personal income or corporate profits. | Limited reporting requirements for non-residents. | No direct tax benefits for residents of other countries, but tax efficiency can be achieved depending on overall tax strategy. |
| Singapore | Tax residency based on number of days spent in Singapore. | Strict reporting requirements. | Tax benefits for certain types of income, but compliance is crucial. |
Successfully setting up and managing an offshore bank account hinges on meticulous planning and a thorough understanding of international regulations. This guide has provided a framework for navigating the complexities involved, from selecting the appropriate jurisdiction and completing the necessary documentation to adhering to best practices for security and compliance. Remember, seeking professional financial and legal advice tailored to your specific circumstances is crucial.
By carefully weighing the benefits and risks, and adhering to best practices, you can leverage the advantages of offshore banking while mitigating potential pitfalls. Proactive management and a commitment to transparency will ensure a smooth and successful experience.