International Bank Account UK: Navigating the complexities of opening and managing an international bank account in the UK can feel daunting, but understanding the process, account types, and associated costs is crucial for both UK residents and expats. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of international banking in the UK, offering clarity on eligibility, application procedures, fees, and tax implications.
Whether you’re a business owner needing efficient international transactions or an individual seeking global financial access, this resource empowers you to make informed decisions.
We’ll explore the various types of international bank accounts available, outlining their features, benefits, and associated fees. We’ll delve into the eligibility criteria, required documentation, and the step-by-step account opening process, covering both online and in-person applications. Crucially, we’ll also examine the important aspects of managing your account, including security, international transfers, currency exchange, and the tax implications for both UK residents and non-residents.
By the end, you’ll be equipped to choose the right bank and confidently manage your international finances in the UK.
Types of International Bank Accounts in the UK
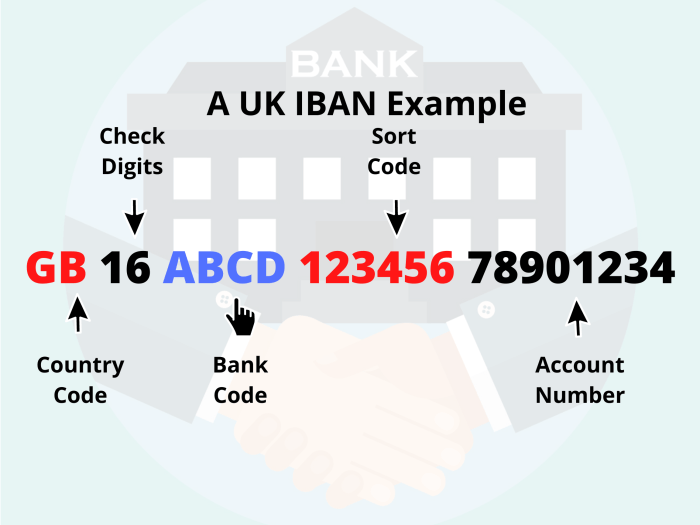
Choosing the right international bank account in the UK depends heavily on your specific financial needs and circumstances. Several account types cater to different requirements, each with its own set of features, benefits, and associated fees. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
Offshore Account
Offshore accounts, while technically not based within the UK, are frequently used by UK residents for international transactions and asset diversification. These accounts are held in jurisdictions with different tax laws and regulations than the UK. The features of an offshore account vary significantly depending on the specific bank and location. They often offer higher levels of privacy compared to domestic accounts, but also carry increased regulatory scrutiny and reporting requirements.
Fees can be substantial, varying based on transaction volume, currency conversion, and account maintenance. Minimum deposit requirements also differ considerably.
International Current Account
International current accounts are designed for regular transactions in multiple currencies. These accounts typically offer features like multi-currency debit cards, online banking access, and international money transfer services. The fees associated with these accounts vary depending on the bank and the level of service offered. Some banks might charge monthly maintenance fees, while others may offer fee-free accounts with conditions.
Minimum deposit requirements are generally lower than for other account types.
International Savings Account
International savings accounts allow you to hold and grow savings in different currencies. These accounts typically offer competitive interest rates, although these rates can fluctuate based on market conditions. Similar to current accounts, fees vary between providers, with some charging monthly maintenance fees or transaction fees. Minimum deposit requirements may be higher than for current accounts to incentivize larger savings balances.
Comparison Table of International Bank Accounts in the UK
| Account Type | Features | Fees | Minimum Deposit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Offshore Account | High privacy, multi-currency options, international transactions | High account maintenance fees, transaction fees, currency conversion fees | Varies significantly, often high |
| International Current Account | Multi-currency debit card, online banking, international money transfers | Monthly maintenance fees (potentially), transaction fees, currency conversion fees (potentially) | Generally low |
| International Savings Account | Multi-currency savings, competitive interest rates | Monthly maintenance fees (potentially), transaction fees | Potentially higher than current accounts |
Eligibility and Requirements
Opening an international bank account in the UK requires meeting specific eligibility criteria and providing comprehensive documentation. The verification process is rigorous, designed to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. Understanding these requirements is crucial for a successful application.
Eligibility Criteria for International Bank Accounts, International Bank Account Uk
Eligibility hinges primarily on demonstrating a genuine need for a UK bank account and providing sufficient evidence of identity, address, and financial standing. Banks generally require applicants to be over 18 years of age and able to demonstrate a legitimate reason for opening an account, such as working in the UK, studying, investing, or owning property. Specific eligibility criteria can vary between banks, with some institutions catering to specific customer profiles, such as high-net-worth individuals or international businesses.
For example, a non-resident might need to show proof of income from a foreign source, while a business applicant would need to provide company registration documents and financial statements.
Required Documentation for Application
A comprehensive set of documents is typically required to support an application. This usually includes a valid passport or national identity card, proof of address (such as a utility bill or bank statement from your home country), and evidence of the purpose of the account. Further documentation may be requested depending on the applicant’s circumstances and the type of account.
For instance, businesses may need to provide their articles of incorporation, tax registration details, and business plan. Applicants should be prepared to provide additional documents if requested by the bank during the verification process.
Verification Process
The verification process aims to confirm the applicant’s identity and the legitimacy of their application. This usually involves identity checks against official databases and thorough scrutiny of the supporting documents. Banks may conduct further due diligence, such as requesting additional documentation or contacting references. The verification process can take several weeks, depending on the complexity of the application and the bank’s internal procedures.
The bank may also use sophisticated fraud detection systems to screen applications and flag potentially suspicious activity.
Reasons for Application Rejection
Applications for international bank accounts can be rejected for various reasons. Common causes include providing incomplete or inaccurate documentation, failing to demonstrate a legitimate need for the account, or having a history of financial irregularities. Applicants with poor credit history in their home country or a history of involvement in suspicious activities may also face rejection. For example, an application might be rejected if the provided address proof is outdated or if the applicant cannot adequately explain the source of their funds.
A lack of sufficient income to maintain the account might also lead to rejection.
Opening an Account
Opening an international bank account in the UK involves several steps, varying slightly depending on the chosen bank and application method. Understanding the process is crucial for a smooth and efficient account opening experience. This section Artikels the typical steps involved, regardless of whether you apply online or in person.
The application process for an international bank account in the UK generally requires providing comprehensive personal and financial information to verify your identity and assess your financial standing. Banks adhere to strict Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations, making thorough verification an essential part of the process.
Online Application Process
Many UK banks offer convenient online account opening options. This method typically involves completing a digital application form and submitting supporting documents electronically. The following steps Artikel a typical online application process:
- Visit the Bank’s Website: Navigate to the chosen bank’s website and locate the international account application section.
- Complete the Application Form: This form will request detailed personal information, including your full name, address, date of birth, nationality, and passport details. You will also need to provide information about your employment, source of funds, and the purpose of the account.
- Upload Supporting Documents: Banks typically require supporting documentation such as a copy of your passport or national ID card, proof of address, and proof of income. Ensure the documents are clear, legible, and in the required format.
- Verify Your Identity: You might be required to undergo identity verification through a third-party service or by video call with a bank representative.
- Account Activation: Once your application is approved, you will receive confirmation and instructions on accessing your new account.
In-Person Application Process
Applying for an international bank account in person at a branch offers the advantage of direct interaction with bank staff, who can guide you through the process and answer any questions you may have. However, it requires scheduling an appointment and visiting a branch in person.
- Schedule an Appointment: Contact the chosen bank to schedule an appointment at a convenient branch location.
- Complete the Application Form: You will be provided with an application form to complete at the branch. This will require the same information as the online application.
- Submit Supporting Documents: Present the required supporting documents, such as a passport, proof of address, and proof of income, to the bank representative.
- Identity Verification: The bank representative will verify your identity using your provided documents and potentially additional verification methods.
- Account Activation: Upon approval, your account will be activated, and you will receive your account details.
Application Process Flowchart
A flowchart illustrating the application process would begin with a starting point “Begin Application”. The next step would be a decision point: “Online or In-Person Application?”. If “Online,” the process would follow the steps Artikeld in the “Online Application Process” section above, culminating in “Account Approved/Rejected”. If “In-Person,” the process would follow the steps Artikeld in the “In-Person Application Process” section, also leading to “Account Approved/Rejected”.
Both paths would then branch to either “Account Activated” or “Application Denied” (with a potential feedback loop for resubmission if denied). The flowchart concludes with an end point “End Application”.
Tax Implications: International Bank Account Uk

Holding an international bank account in the UK has significant tax implications, varying considerably depending on your residency status and the nature of your financial activities. Understanding these implications is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with UK tax laws. Failure to correctly report income generated through or held within these accounts can lead to substantial fines and legal repercussions.The UK tax system operates on a self-assessment basis, meaning individuals are responsible for accurately declaring their income and capital gains.
This applies equally to UK residents and non-residents with UK-based financial assets. The complexity increases when dealing with international accounts due to the potential for double taxation agreements and differing reporting requirements between countries.
Tax Implications for UK Residents
UK residents are taxed on their worldwide income and capital gains. This means any income earned or capital gains realised from investments held in an international bank account are taxable in the UK, regardless of where the account is held. This includes interest earned on deposits, dividends from shares, and profits from trading activities. The applicable tax rates depend on the individual’s overall income and the type of income generated.
For example, interest income is typically taxed as savings income, while capital gains are subject to capital gains tax rates. Careful record-keeping is essential to accurately calculate the tax liability. Tax relief may be available under certain circumstances, such as double taxation relief where tax has already been paid on the same income in another country.
Tax Implications for Non-UK Residents
Non-UK residents are generally only taxed on UK-sourced income. This means that income generated from sources within the UK, such as interest from UK-based bonds held in their international account, would be subject to UK tax. Income generated outside the UK from assets held in their international account is typically not taxable in the UK. However, this is subject to the specific terms of any applicable double taxation agreements between the UK and the non-resident’s country of residence.
Understanding these agreements is crucial for accurate tax reporting. Non-residents should seek professional tax advice to determine their precise tax obligations.
Reporting Requirements
Both UK residents and non-residents with international bank accounts are required to report relevant information to HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). This reporting typically involves completing self-assessment tax returns and declaring all relevant income and capital gains. For UK residents, this is a mandatory annual requirement. For non-residents, reporting obligations depend on the specific circumstances and the type of income received.
Failure to report income or provide accurate information can result in significant penalties. HMRC actively monitors international financial transactions, and information sharing agreements with other countries further enhance their ability to detect tax evasion.
Examples of Tax Scenarios
Scenario 1: A UK resident earns £10,000 in interest from a foreign bank account. This interest is taxable in the UK and will be included in their self-assessment tax return. The applicable tax rate will depend on their overall income level.Scenario 2: A non-UK resident earns £5,000 in dividends from UK-based shares held in an offshore account. This dividend income is taxable in the UK.
The tax liability will be determined based on the applicable UK tax rates for non-residents.Scenario 3: A UK resident sells shares held in an international account, resulting in a capital gain of £20,000. This capital gain is subject to UK capital gains tax. The amount of tax payable will depend on their total capital gains for the tax year and any allowable exemptions or reliefs.
Currency Exchange and International Transfers
Managing currency exchange and international transfers is a crucial aspect of maintaining an international bank account in the UK. Understanding the processes, associated costs, and best practices can significantly impact the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of your international financial transactions. This section details the mechanics of these processes and provides strategies for optimizing your international money management.
Exchanging currencies and making international transfers involves several steps. First, you’ll need to determine the amount of money you wish to transfer and the target currency. Your bank will then apply its exchange rate, which is usually slightly less favorable than the mid-market rate (the average of the buy and sell rates). The transfer itself can be initiated through various methods, each with its own processing time and associated fees.
Once initiated, the transfer will be processed through the relevant international payment systems, eventually reaching the recipient’s account. The entire process, depending on the method used, can take anywhere from a few hours to several business days.
Methods of International Money Transfer
Several methods exist for transferring money internationally, each offering a different balance between speed, cost, and convenience. The choice depends largely on the urgency of the transfer, the amount involved, and the recipient’s location and banking arrangements.
- Bank Transfers: Traditional bank transfers are generally reliable but can be slower and more expensive than other methods. Fees vary depending on the bank and the transfer amount. Exchange rates offered by banks are usually less favorable than those available through specialized providers.
- Online Money Transfer Services: Services like Wise (formerly TransferWise), WorldRemit, and PayPal offer competitive exchange rates and often lower fees than banks. They usually provide faster transfer times than traditional bank transfers. However, some services may impose limits on the amount you can transfer at once.
- International Payment Networks: SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) is a widely used network for international bank transfers. While reliable, transfers through SWIFT can be slow and subject to higher fees.
Fees and Exchange Rates
Understanding the fees and exchange rates associated with international transfers is critical for cost management. Banks and money transfer services typically charge fees based on the transfer amount and the destination country. These fees can vary significantly, so comparing options before making a transfer is essential. Additionally, the exchange rate used will impact the final amount received by the recipient.
Banks often apply a markup to the mid-market rate, resulting in a less favorable exchange rate for the customer.
| Transfer Method | Typical Fee | Exchange Rate | Transfer Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank Transfer | £10-£50+ | Less favorable than mid-market | 3-5 business days |
| Online Money Transfer Service | £1-£20 | Close to mid-market | 1-3 business days |
| SWIFT Transfer | £20-£100+ | Less favorable than mid-market | 3-5 business days |
Minimizing Costs and Maximizing Efficiency
Several strategies can help minimize costs and improve the efficiency of international money transfers. These strategies aim to reduce fees and obtain more favorable exchange rates.
- Compare Exchange Rates and Fees: Before initiating a transfer, compare the exchange rates and fees offered by different providers. Use online comparison tools to find the best deal.
- Transfer Larger Amounts Less Frequently: Transferring larger sums less often can reduce the overall cost of fees, as many providers charge fixed fees regardless of the transfer amount (up to a certain limit).
- Utilize Online Money Transfer Services: These services often offer more competitive exchange rates and lower fees than traditional banks.
- Choose the Right Transfer Method: Select the transfer method that best balances speed, cost, and convenience based on your specific needs.
- Consider Mid-Market Exchange Rates: Use online converters to check the mid-market exchange rate and compare it to the rate offered by your chosen provider to assess the markup.
Choosing the Right Bank
Selecting the appropriate bank for an international account in the UK requires careful consideration of several key factors. The ideal institution will offer a competitive suite of features, transparent and reasonable fees, and reliable customer service tailored to the needs of international clients. Failing to thoroughly research your options can lead to unnecessary expenses and complications in managing your finances.Choosing the right bank hinges on a careful evaluation of your specific financial needs and priorities.
This includes assessing your transaction volume, the currencies you’ll be working with, and the level of customer support you anticipate requiring. Factors such as the bank’s international network, online banking capabilities, and the availability of multilingual support should also be weighed.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Bank
Several crucial factors influence the selection of a suitable bank for an international account. These factors should be meticulously assessed to ensure the chosen institution aligns with your individual financial circumstances and requirements.
| Bank Name | Features | Fees | Customer Service Ratings |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSBC | Extensive global network, online and mobile banking, multi-currency accounts | Variable, depending on account type and services used; potential for high fees on international transfers. | Generally high ratings, but experiences can vary. |
| Barclays | Wide range of accounts, strong online platform, decent international transfer options. | Competitive fees, but specific charges vary depending on account type and transaction. | Generally positive customer service reviews, although some complaints exist regarding response times. |
| NatWest | International money transfer services, online banking, various account options. | Fees vary according to account type and services. Transparency regarding fees is generally considered good. | Customer service ratings are generally average, with some areas for improvement noted. |
| Lloyds Bank | Established bank with a solid online presence, international transfer capabilities. | Fees are competitive but can vary significantly based on the services used and the account type. | Customer service experiences are mixed, with some reporting positive interactions and others noting difficulties. |
Comparison of Banks Based on Features, Fees, and Customer Service
Direct comparison of banks based on these three key aspects is crucial for informed decision-making. The following table offers a simplified comparison, but individual experiences may vary. It’s recommended to consult the official websites of each bank for the most up-to-date information on fees and services. Independent review sites can also provide valuable insights into customer service experiences.
Opening an International Bank Account UK presents a strategic opportunity for global financial management. By carefully considering the various account types, understanding the application process, and diligently managing your account, you can leverage the benefits of international banking to streamline your financial operations and achieve your international financial goals. Remember to thoroughly research different banks, compare their offerings, and choose the option that best aligns with your specific needs and financial objectives.
Proactive planning and a clear understanding of the associated fees and tax implications will ensure a smooth and successful banking experience.

