Offshore Bank Account In Usa: Navigating the complex world of offshore banking as a US citizen requires careful consideration of legal, financial, and logistical factors. This guide unravels the intricacies of establishing and managing an offshore account, exploring the potential benefits and risks involved. From understanding the regulatory landscape and choosing the right account type to selecting a reputable bank and mitigating potential challenges, we provide a comprehensive overview to empower informed decision-making.
This in-depth exploration covers the legality and regulations surrounding offshore accounts for US citizens, detailing tax implications and reporting requirements. We’ll examine various account types, their features, and associated costs, guiding you through the process of opening and managing an account from the US. Furthermore, we’ll analyze the potential financial advantages, such as asset protection and diversification, alongside the inherent risks, including currency fluctuations and political instability.
Finally, we’ll profile reputable offshore banks and present real-world scenarios to illustrate the practical applications and potential pitfalls of offshore banking.
Legality and Regulations of Offshore Bank Accounts for US Citizens
US citizens are permitted to hold offshore bank accounts, but doing so necessitates strict adherence to US tax laws and reporting requirements. The legal framework governing these accounts is complex and designed to prevent tax evasion and money laundering. Understanding these regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain compliance.
US Tax Implications of Offshore Accounts
The primary legal concern for US citizens with offshore accounts is tax compliance. The Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR) requires US taxpayers with financial interests in or signature authority over foreign accounts exceeding $10,000 at any point during the calendar year to file an FBAR with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). Failure to file an FBAR can result in significant penalties, including substantial fines and even criminal prosecution.
Furthermore, all income earned in these accounts, regardless of whether it is distributed, is subject to US taxation. This income must be reported on Form 8938, Statement of Specified Foreign Financial Assets, if the aggregate value of specified foreign financial assets exceeds certain thresholds. Properly completing and filing these forms is vital to demonstrating compliance.
Reporting Requirements for Offshore Accounts
Beyond the FBAR and Form 8938, US citizens must also comply with other reporting requirements depending on the type of account and the nature of the assets held. This might include reporting on Form 1040, Schedule B (Interest and Ordinary Dividends) for interest earned, or Schedule D (Capital Gains and Losses) for capital gains realized on investments held in the offshore account.
The complexity of reporting increases with the diversity of assets held within the offshore account. For example, a US citizen holding stocks and bonds within an offshore account would need to report both capital gains and dividends on their US tax return.
Regulations for Different Types of Offshore Accounts
The regulations governing offshore accounts vary depending on the type of account. For example, a simple savings account will have different reporting requirements compared to a more complex investment account holding stocks, bonds, or other assets. Similarly, accounts held in tax havens may attract increased scrutiny from tax authorities. Understanding the specific regulations for the type of offshore account held is critical for compliance.
Examples of Legally Permissible and Problematic Offshore Account Holdings
Holding an offshore account can be legally permissible in situations such as managing foreign investments, receiving inheritance from foreign sources, or operating a legitimate business overseas. However, using an offshore account to conceal assets from tax authorities or engage in illicit activities, such as money laundering, is strictly prohibited and carries severe legal consequences. For example, a US citizen working abroad and earning income in a foreign country may legitimately hold an offshore account to manage those earnings.
Conversely, a US citizen using an offshore account to hide undeclared income from US tax authorities would be committing a serious offense.
Key Legal Considerations for US Citizens Considering Offshore Banking
| Aspect | Requirement | Consequences of Non-Compliance | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Reporting | File FBAR (if applicable), Form 8938, and report all income | Significant fines, criminal prosecution | Failing to report interest earned on an offshore savings account. |
| Account Type | Understand specific regulations for the type of account | Incorrect reporting, potential penalties | Misreporting capital gains from an offshore investment account. |
| Asset Reporting | Report all assets held in the offshore account | Underreporting of assets, tax evasion charges | Failing to disclose holdings of foreign stocks and bonds. |
| Transparency | Maintain accurate records and documentation | Difficulty in demonstrating compliance | Lack of supporting documentation for foreign income or transactions. |
Reputable Offshore Banks and Their Services
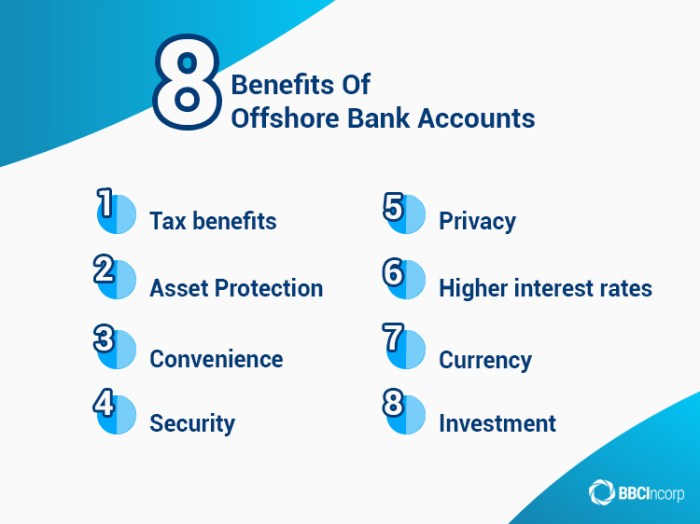
Choosing an offshore bank requires careful consideration of reputation, services, and regulatory compliance. While the term “offshore” can sometimes carry negative connotations, many reputable institutions operate internationally and offer services to US citizens who meet their eligibility criteria. It’s crucial to understand that these banks are subject to their own country’s regulations, and compliance with US tax laws remains the responsibility of the US citizen.
Several factors influence the selection of an offshore bank, including the types of accounts offered, associated fees, the level of customer support provided, and the bank’s overall financial stability and reputation. Understanding these factors allows for a more informed decision-making process. This section will explore some reputable offshore banks and their services, providing a comparative analysis to aid in your research.
Services Offered by Reputable Offshore Banks
Reputable offshore banks offer a range of services designed to cater to the diverse needs of international clients, including US citizens. These services typically include various account types, tailored investment options, and dedicated customer support channels. The specific services available may vary depending on the bank and the client’s individual circumstances. However, common offerings include personal and business accounts, wealth management solutions, and currency exchange services.
Fees associated with these services can vary significantly based on the account type, transaction volume, and the specific bank’s fee structure. It is essential to carefully review the fee schedule before opening an account.
Comparison of Reputable Offshore Banks
The following table compares three reputable offshore banks, highlighting key features and fees. Note that this information is for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct thorough independent research before making any financial decisions. Fees and services are subject to change.
| Bank Name | Account Types | Minimum Deposit | Annual Fee (Example) | Customer Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Bank A (Jurisdiction: [Insert Jurisdiction]) | Personal, Business, Investment | USD 50,000 | USD 500 (Variable based on balance) | Online banking, phone, email |
| Example Bank B (Jurisdiction: [Insert Jurisdiction]) | Personal, Business, Savings, Fixed Deposit | USD 25,000 | USD 250 (Variable based on balance) | Online banking, phone, email, in-person (select locations) |
| Example Bank C (Jurisdiction: [Insert Jurisdiction]) | Personal, Business, Corporate | USD 100,000 | USD 1000 (Fixed) | Online banking, phone, email, dedicated relationship manager |
Disclaimer: The banks and information presented above are for illustrative purposes only and do not constitute an endorsement. The specific services, fees, and minimum deposit requirements are subject to change and should be verified directly with the respective banks. It is crucial to conduct thorough due diligence before engaging with any offshore banking institution.
Illustrative Scenarios: Offshore Bank Account In Usa
Understanding the complexities of offshore banking for US citizens requires examining real-world applications. The following scenarios illustrate both the potential benefits and significant risks associated with establishing and maintaining an offshore bank account. Careful consideration of legal and tax implications is paramount in each instance.
Estate Planning Utilizing an Offshore Account
A US citizen with significant assets, including real estate holdings in multiple countries and substantial investment portfolios, might establish an offshore trust in a jurisdiction with favorable estate tax laws. This trust would hold a portion of their assets, managed by professional trustees, and distribute income or principal to beneficiaries according to a pre-determined plan. The offshore account, linked to the trust, facilitates efficient management and distribution of these international assets, minimizing potential estate taxes and simplifying the inheritance process for heirs.
This strategy is often employed to minimize estate taxes, particularly when assets are located internationally, and simplifies the probate process across multiple jurisdictions. The specific tax advantages would depend on the chosen jurisdiction and the structure of the trust, requiring expert legal and tax advice.
International Business Transactions and Offshore Accounts
A US citizen operating an international import/export business might use an offshore account to streamline transactions with foreign suppliers and clients. This account facilitates currency exchange, reduces transaction fees associated with international wire transfers, and improves the overall efficiency of managing international funds. For example, a US company importing goods from China might receive payments from Chinese clients directly into an offshore account denominated in the Chinese Yuan (CNY), thus avoiding multiple currency conversions and associated fees.
However, meticulous record-keeping and compliance with US tax laws, including reporting of foreign bank accounts (FBAR), are essential to avoid penalties.
Pitfalls of Offshore Banking Without Proper Advice, Offshore Bank Account In Usa
A US citizen, seeking to avoid US taxes, opens an offshore account without seeking professional legal and tax advice. They fail to properly report the account to the IRS, resulting in significant penalties and potential criminal charges. This scenario highlights the crucial role of qualified professionals in navigating the complex legal and tax landscape surrounding offshore banking. The individual’s actions, motivated by tax avoidance, resulted in far greater financial liabilities than they intended to avoid.
The penalties could include significant fines, interest charges, and potential criminal prosecution for tax evasion.
Complexities of Managing an Offshore Bank Account
A US citizen, owning a business with operations in multiple countries, maintains an offshore account to manage international payments. However, the complexities of currency exchange rates, differing banking regulations, and the need for meticulous record-keeping to comply with both US and foreign regulations present significant challenges. The individual faces difficulties in managing the account due to language barriers, different time zones, and the need to navigate varying banking practices and reporting requirements.
This situation emphasizes the need for specialized financial management expertise and potentially the use of international banking professionals to assist in navigating these complex issues. Furthermore, ensuring compliance with all relevant reporting requirements, such as FBAR and FATCA, adds a further layer of complexity.
Establishing an offshore bank account as a US citizen presents a multifaceted decision with significant financial and legal ramifications. While potential benefits like asset protection and international diversification exist, understanding and adhering to all regulations is paramount to avoid legal and tax complications. This guide has provided a framework for navigating this complex landscape, emphasizing the importance of thorough research, professional advice, and careful consideration of both the potential rewards and risks involved.
Remember, proactive planning and informed choices are crucial for successfully managing offshore finances.

